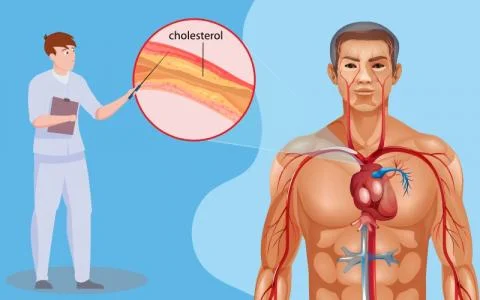
High cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance essential for various bodily functions, such as building cells, producing hormones, and synthesizing vitamin D. However, excessive cholesterol levels can lead to severe health issues, particularly cardiovascular diseases.
Types of Cholesterol:
- LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein): Known as "bad" cholesterol, it can accumulate in artery walls, forming plaques and causing blockages.
- HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein): Known as "good" cholesterol, it helps remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream.
Symptoms of High Cholesterol:
High cholesterol often presents no obvious symptoms, earning it the label of a "silent condition." However, prolonged elevated levels may lead to complications, including:
- Xanthomas: Yellowish fatty deposits under the skin or around the eyes.
- Corneal Arcus: A white or gray ring around the cornea, typically in older adults.
- Chest Pain (Angina): Caused by blocked arteries.
- Leg Pain: Cramping during physical activity due to reduced blood flow.
Associated Diseases:
- Atherosclerosis: Plaque buildup in arteries, reducing blood flow.
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Blocked heart arteries, increasing heart attack risk.
- Hypertension: High blood pressure caused by restricted blood flow.
Diagnosis:
A Lipid Profile Test measures:
- Total Cholesterol: <200 mg/dL.
- LDL: <100 mg/dL.
- HDL: >40 mg/dL (men), >50 mg/dL (women).
- Triglycerides: <150 mg/dL.
Treatment for High Cholesterol:
1. Lifestyle Changes:
- Diet:
- Avoid trans fats and reduce saturated fats (found in red meat and full-fat dairy).
- Include omega-3-rich foods (salmon, walnuts, flaxseeds).
- Increase fiber intake with oats, fruits, vegetables, and legumes.
- Exercise: Engage in 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise (walking, cycling) at least 5 days a week.
- Weight Management: Losing 5-10% of body weight significantly lowers cholesterol levels.
- Quit Smoking: Boosts HDL levels and lowers heart disease risk.
- Limit Alcohol: Excessive consumption raises cholesterol and triglycerides.
2. Medications:
- Statins: Reduce LDL cholesterol (e.g., Atorvastatin, Rosuvastatin).
- Ezetimibe: Limits cholesterol absorption in the intestine.
- PCSK9 Inhibitors: Injectable medications for significantly lowering LDL (e.g., Alirocumab, Evolocumab).
- Bile Acid Sequestrants: Promote bile acid excretion (e.g., Cholestyramine).
- Fibrates: Lower triglycerides and modestly increase HDL (e.g., Fenofibrate).
- Niacin: Helps increase HDL cholesterol.
3. Alternative Therapies (consult your doctor before starting):
- Omega-3 fatty acids, garlic extract, or plant sterol supplements.
Complications of Untreated High Cholesterol:
- Heart Attack: Due to blocked coronary arteries.
- Stroke: Caused by restricted blood flow to the brain.
- Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): Severe limb pain or potential amputation.
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Reduced kidney blood supply.
Prevention:
- Follow a balanced diet low in saturated fats and rich in fiber.
- Engage in regular physical activity.
- Periodically monitor cholesterol levels, especially with a family history.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption.
- Manage diabetes and hypertension to mitigate associated risks.
Hot Categories
Recent News
Politics
Mahila Samman Yojana: A Revolutionary Initiative Launched in Delhi
- 13 January, 2025
- 11 months ago
Entertainment
Maha Kumbh 2025: Shankar Mahadevan & Kailash Kher To Enchant Prayagraj With Soulful Music
- 13 January, 2025
- 11 months ago









